Raft 笔记(五) – Log replication
Log compaction
在 basic 中只提到了 log replication,但是随着时间的推移,log 越来越多,会对可用性造成影响:
- 耗尽磁盘空间;
- 重启或新加入的节点需要很长时间来恢复数据。
需要通过 snapshot 来清理 log:
- 把状态机的当前状态写入 snapshot 中,然后清理相应的 log。同时需要记录 snapshot 中最后一个 entry 的 index 和 term 用于 AppendEntries 的 check 和 snapshot 与 log 的比较。
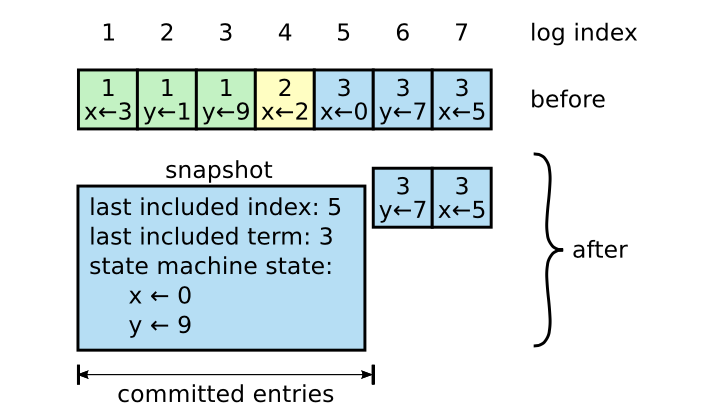
当增加了 snapshot 之后,发送 log 的过程如下:
leader的next记录了需要发送给follower的下一个entry;- 若
next仍在log中,则发送后续的entries; - 若
next在snapshot中,则发送snapshot,发送成功后,再发送后续的entries; follower收到snapshot时,如果log与snapshot有冲突或者snapshot比log新,则丢弃全部log,应用snapshot。
每个节点独立的选择何时做 snapshot,而不是由 leader 统一发起 snapshot:
snapshot只清理committed log,每个节点有能力独立的做snapshot,不会带来一致性问题;- 如果由
leader做snapshot然后发送给其他节点,会浪费网络带宽; - 每个节点的配置和状态可能不同,可以独立选择合适的时机做
snapshot。
Storage
Raft 只保证 log 的一致性,如何存储 log 和如何做 snapshot 由状态机负责,需要把存储从 Raft 中解耦出来:
etcd/raft抽象出Storage接口由用户实现,Storage提供了查询持久存储的接口:// Storage is an interface that may be implemented by the application // to retrieve log entries from storage. // // If any Storage method returns an error, the raft instance will // become inoperable and refuse to participate in elections; the // application is responsible for cleanup and recovery in this case. type Storage interface { // InitialState returns the saved HardState and ConfState information. InitialState() (pb.HardState, pb.ConfState, error) // Entries returns a slice of log entries in the range [lo,hi). // MaxSize limits the total size of the log entries returned, but // Entries returns at least one entry if any. Entries(lo, hi, maxSize uint64) ([]pb.Entry, error) // Term returns the term of entry i, which must be in the range // [FirstIndex()-1, LastIndex()]. The term of the entry before // FirstIndex is retained for matching purposes even though the // rest of that entry may not be available. Term(i uint64) (uint64, error) // LastIndex returns the index of the last entry in the log. LastIndex() (uint64, error) // FirstIndex returns the index of the first log entry that is // possibly available via Entries (older entries have been incorporated // into the latest Snapshot; if storage only contains the dummy entry the // first log entry is not available). FirstIndex() (uint64, error) // Snapshot returns the most recent snapshot. // If snapshot is temporarily unavailable, it should return ErrSnapshotTemporarilyUnavailable, // so raft state machine could know that Storage needs some time to prepare Snapshot() (pb.Snapshot, error) }unstable管理非持久存储(内存),节点收到log或snapshot先存放在unstable中,然后通过Ready返回给用户,用户处理完成后调用node.Advance()通知raft进行清理:// unstable.entries[i] has raft log position i+unstable.offset. // Note that unstable.offset may be less than the highest log // position in storage; this means that the next write to storage // might need to truncate the log before persisting unstable.entries. type unstable struct { // the incoming unstable snapshot, if any. snapshot *pb.Snapshot // all entries that have not yet been written to storage. entries []pb.Entry offset uint64 logger Logger }Storage和unstable构成raftLog结构管理整个存储:type raftLog struct { // storage contains all stable entries since the last snapshot. storage Storage // unstable contains all unstable entries and snapshot. // they will be saved into storage. unstable unstable // committed is the highest log position that is known to be in // stable storage on a quorum of nodes. committed uint64 // applied is the highest log position that the application has // been instructed to apply to its state machine. // Invariant: applied <= committed applied uint64 logger Logger }
Progress
etcd/raft 使用 Progress 结构管理每个节点的状态与进度,同时还有流控的功能,参考 progress 文档:
// Progress represents a follower’s progress in the view of the leader. Leader maintains
// progresses of all followers, and sends entries to the follower based on its progress.
type Progress struct {
Match, Next uint64
// State defines how the leader should interact with the follower.
//
// When in ProgressStateProbe, leader sends at most one replication message
// per heartbeat interval. It also probes actual progress of the follower.
//
// When in ProgressStateReplicate, leader optimistically increases next
// to the latest entry sent after sending replication message. This is
// an optimized state for fast replicating log entries to the follower.
//
// When in ProgressStateSnapshot, leader should have sent out snapshot
// before and stops sending any replication message.
State ProgressStateType
// Paused is used in ProgressStateProbe.
// When Paused is true, raft should pause sending replication message to this peer.
Paused bool
// PendingSnapshot is used in ProgressStateSnapshot.
// If there is a pending snapshot, the pendingSnapshot will be set to the
// index of the snapshot. If pendingSnapshot is set, the replication process of
// this Progress will be paused. raft will not resend snapshot until the pending one
// is reported to be failed.
PendingSnapshot uint64
// RecentActive is true if the progress is recently active. Receiving any messages
// from the corresponding follower indicates the progress is active.
// RecentActive can be reset to false after an election timeout.
RecentActive bool
// inflights is a sliding window for the inflight messages.
// Each inflight message contains one or more log entries.
// The max number of entries per message is defined in raft config as MaxSizePerMsg.
// Thus inflight effectively limits both the number of inflight messages
// and the bandwidth each Progress can use.
// When inflights is full, no more message should be sent.
// When a leader sends out a message, the index of the last
// entry should be added to inflights. The index MUST be added
// into inflights in order.
// When a leader receives a reply, the previous inflights should
// be freed by calling inflights.freeTo with the index of the last
// received entry.
ins *inflights
// IsLearner is true if this progress is tracked for a learner.
IsLearner bool
}
每个 follower 会处于下面三种状态之一,状态转换如下图:
Probe:leader不知道该节点的log情况,需要找到匹配的log entry。发生在新选举出的leader或AppendEntries冲突时;Replicate: 正常复制状态;Snapshot: 该节点比较落后,需要发送snapshot。+--------------------------------------------------------+ | send snapshot | | | +---------+----------+ +----------v---------+ +---> probe | | snapshot | | | max inflight = 1 <----------------------------------+ max inflight = 0 | | +---------+----------+ +--------------------+ | | 1. snapshot success | | (next=snapshot.index + 1) | | 2. snapshot failure | | (no change) | | 3. receives msgAppResp(rej=false&&index>lastsnap.index) | | (match=m.index,next=match+1) receives msgAppResp(rej=true) (next=match+1)| | | | | | | | receives msgAppResp(rej=false&&index>match) | | (match=m.index,next=match+1) | | | | | | | +---------v----------+ | | replicate | +---+ max inflight = n | +--------------------+
Probe
新选举出的 leader 设置每个节点为 Probe 状态、match = 0、next = last index + 1:
r.forEachProgress(func(id uint64, pr *Progress) {
*pr = Progress{Next: r.raftLog.lastIndex() + 1, ins: newInflights(r.maxInflight), IsLearner: pr.IsLearner}
if id == r.id {
pr.Match = r.raftLog.lastIndex()
}
})
并且会添加一个当前 term 的空 entry,立即发送 msgApp 给所有节点,有两个作用:
- 为了提交之前
term的log entries:Raft只会提交当前term的log,若之后一直没新请求,则之前term未提交的log一直不会提交。 - 更新
leader的committed index:Raft按照log新旧来选举,而不是committed index,所以新选举出的leader的committed index可能会落后,影响一致性。
leader 在 msgApp 中设置上一条 entry 的 term 和 index 用于 follower 匹配,当发生冲突时,follower 返回的 MsgAppResp 会携带冲突的 index 和自己的 last index(跳过不存在的 log):
r.send(pb.Message{To: m.From, Type: pb.MsgAppResp, Index: m.Index, Reject: true, RejectHint: r.raftLog.lastIndex()})
对于 Probe 状态的冲突,采用的是每次回退一条的策略:next = min(rejected, peerLastIndex + 1),因为在生产环境中,发生错误的频率很低,且不一致的 log 很少。
当 follower 接受 msgApp 时,变为 Replicate 状态,进行正常的 log replication;当 next 落入 snapshot 中,会变为 Snapshot 状态,发送 Snapshot。
Replicate
当 Probe 状态的节点接受 msgApp 时,变为 Replicate 状态。对于 Replicate 状态的节点,leader 采用 pipeline 方式发送 msgApp,直接增加 next,不用等到接收响应。
follower 在消息中返回新添加的 entries 的 last index,用于 leader 更新节点的 match。
节点有可能收到与当前 log 冲突的 msgApp,需要进行 truncate。unstable 中只保存未写入持久存储的 log,unstable.offset 之前的 log 都已经写入持久存储。当 log 发生冲突时:
- 若只在
unstable中,只是truncate内存中的slice; - 若在持久存储中,会重置
unstable.offset和unstable.entries,然后在Ready中返回,由用户truncate:// ents 为需要 append 的 entries func (u *unstable) truncateAndAppend(ents []pb.Entry) { after := ents[0].Index switch { case after == u.offset+uint64(len(u.entries)): // after is the next index in the u.entries // directly append u.entries = append(u.entries, ents...) case after <= u.offset: u.logger.Infof("replace the unstable entries from index %d", after) // The log is being truncated to before our current offset // portion, so set the offset and replace the entries u.offset = after u.entries = ents default: // truncate to after and copy to u.entries // then append u.logger.Infof("truncate the unstable entries before index %d", after) u.entries = append([]pb.Entry{}, u.slice(u.offset, after)...) u.entries = append(u.entries, ents...) } }
当 majority 的节点接收了 log 时就会 commit:
// maybeCommit attempts to advance the commit index. Returns true if
// the commit index changed (in which case the caller should call
// r.bcastAppend).
func (r *raft) maybeCommit() bool {
// TODO(bmizerany): optimize.. Currently naive
mis := make(uint64Slice, 0, len(r.prs))
for _, p := range r.prs {
mis = append(mis, p.Match)
}
sort.Sort(sort.Reverse(mis))
mci := mis[r.quorum()-1]
return r.raftLog.maybeCommit(mci, r.Term)
}
committed entries 同样通过 Ready 返回给用户。Node.Advance() 会更新 applied。
Snapshot
当 Probe 状态的节点的 next 落在 snapshot 中,变为 Snapshot 状态。leader 发送的 snapshot 中包含最后一条 entry 的 index 和 term,用于 follower 判断 snapshot 新旧。
follower 不会拒绝 snapshot,返回 msgAppResp,用于 leader 更新 match 和 next:
func (r *raft) handleSnapshot(m pb.Message) {
sindex, sterm := m.Snapshot.Metadata.Index, m.Snapshot.Metadata.Term
if r.restore(m.Snapshot) {
r.logger.Infof("%x [commit: %d] restored snapshot [index: %d, term: %d]",
r.id, r.raftLog.committed, sindex, sterm)
r.send(pb.Message{To: m.From, Type: pb.MsgAppResp, Index: r.raftLog.lastIndex()})
} else {
r.logger.Infof("%x [commit: %d] ignored snapshot [index: %d, term: %d]",
r.id, r.raftLog.committed, sindex, sterm)
r.send(pb.Message{To: m.From, Type: pb.MsgAppResp, Index: r.raftLog.committed})
}
}
对于不同新旧的 snapshot 处理方式不同:
- 忽略旧的
snapshot:if s.Metadata.Index <= r.raftLog.committed { return false } - 与自己
log匹配的snapshot,更新commited index。这里与raft论文介绍的不同,raft论文里会保存snapshot,然后删除对应的log,这里只更新committed index,snapshot还是由 状态机自己执行:if r.raftLog.matchTerm(s.Metadata.Index, s.Metadata.Term) { r.logger.Infof("%x [commit: %d, lastindex: %d, lastterm: %d] fast-forwarded commit to snapshot [index: %d, term: %d]", r.id, r.raftLog.committed, r.raftLog.lastIndex(), r.raftLog.lastTerm(), s.Metadata.Index, s.Metadata.Term) r.raftLog.commitTo(s.Metadata.Index) return false } - 其余的
snapshot要么比自己新、要么有冲突,删除unstable中所有的log,更新committed index,然后在Ready中返回,由用户清理持久存储中的log和snapshot,存储新的snapshot, 并将snapshot应用到状态机。func (l *raftLog) restore(s pb.Snapshot) { l.logger.Infof("log [%s] starts to restore snapshot [index: %d, term: %d]", l, s.Metadata.Index, s.Metadata.Term) l.committed = s.Metadata.Index l.unstable.restore(s) }
Snapshot 状态之后会变为 Probe 状态,有两种方式:
- 接收到节点的
msgAppResp; - 用户在发送完
snapshot后调用Node.ReportSnapshot(),告诉leader发送情况:- 发送成功后,更新
next为snapshot的last index + 1; - 发送失败,恢复到原来的
Probe状态,之后会重新发送snapshot。func stepLeader(r *raft, m pb.Message) error { // ... case pb.MsgSnapStatus: if pr.State != ProgressStateSnapshot { return nil } if !m.Reject { pr.becomeProbe() r.logger.Debugf("%x snapshot succeeded, resumed sending replication messages to %x [%s]", r.id, m.From, pr) } else { pr.snapshotFailure() pr.becomeProbe() r.logger.Debugf("%x snapshot failed, resumed sending replication messages to %x [%s]", r.id, m.From, pr) } // If snapshot finish, wait for the msgAppResp from the remote node before sending // out the next msgApp. // If snapshot failure, wait for a heartbeat interval before next try pr.pause() // ... }
- 发送成功后,更新
snapshot 发送的代价较大:
- 应避免频繁发送
snapshot,Progress限制了每次只有 1 个正在发送的snapshot,只有当发送成功或调用Node.ReportSnapshot()发送失败后, 变为Probe状态,才有可能发送下一个snapshot; etcd/raft中snapshot放在单条msg中,一般RPC都对消息大小有限制,可以分为多个RPC并带上offset,或者拆分为多个chunk来发送。
流控
Progress 还有流控的功能:限制发送给 Replication 状态节点消息的数量,而 Config.MaxSizePerMsg 限制了每条消息的大小。流控是必要的,如果发生网络分区,leader 可能会累积很多消息,
当网络恢复,会一下发送很多消息给 follower,可能造成消息丢弃或重传。通过配置 inflights 的大小,可以避免溢出 transportation layer 的发送缓冲区:
- 每次发送
msgApp,会记录消息的last index:pr.ins.add(last) - 当收到
msgAppResp时,释放之前消息占用的空间:pr.ins.freeTo(m.Index) - 当
pr.ins.full()时,会暂停发送。
msgApp 发送的时机
- 正常工作的流程比较简单(
Replicate状态):- 每次调用
Node.Propose()时,leader给所有节点发送msgApp复制entry;(pipeline) - 在更新
committed index时,leader给所有节点发送msgApp更新committed index。
- 每次调用
- 对于处于
Probe状态的节点,采用串行的方式,只有收到上一条消息的响应后,才会发送新的msgApp,因为需要msgAppResp来更新next。 - 对于处于
Snapshot状态的节点,不会发送msgApp。// IsPaused returns whether sending log entries to this node has been // paused. A node may be paused because it has rejected recent // MsgApps, is currently waiting for a snapshot, or has reached the // MaxInflightMsgs limit. func (pr *Progress) IsPaused() bool { switch pr.State { case ProgressStateProbe: return pr.Paused case ProgressStateReplicate: return pr.ins.full() case ProgressStateSnapshot: return true default: panic("unexpected state") } }
但是消息有可能发送超时或失败,或者节点落后较多需要发送多条 msgApp,这里在收到 MsgHeartbeatResp 时会给落后的节点发送 msgApp,相当于定时给落后的节点发消息:
if pr.Match < r.raftLog.lastIndex() {
r.sendAppend(m.From)
}
优化
一次请求 Raft 需要做如下流程:
leader收到client的请求;leader把entry写入持久存储;leader发送replication message给follower;follower接收之后,把entry写入持久存储,然后给leader发送响应;leader等待follower的响应,若majority节点接收了,则apply;leader将结果返回给client。
如果按照上面这种流程,性能会很差,需要进行优化。
Batch
Batch 是等待 request 到达一定数量或者等待超时再进行处理,能够充分利用 I/O。etcd/raft 支持 Batch,分为2个方面:
- 网络:在一条
msgApp中附加多个log entries(大小在Config.MaxSizePerMsg范围内); - 磁盘:
Node.Ready()返回自上次调用时累积的所有entry。
Batch 具体的执行还是要由用户负责:
- 何时调用
Node.Ready()和Node.Advance(); - 何时发送
message。
需要对 batch size 和超时时间进行权衡,如果一直达不到 batch size 就会等到超时才发送,latency 就会很高。
Pipeline
pipeline 指的是 leader 给 follower 发送完 msgApp 立刻更新 next,不用等到 follower 返回响应就可以发送下一个 msgApp。在网络正常的时候,
消息按序到达,pipeline 能够极大的提高吞吐量。虽然单个 TCP 连接能够提供可靠的消息传递,但是 etcd/raft 是一个通用的库,不能依赖客户的实现,
即使使用单个 TCP 连接,节点仍有可能收到乱序的、过时的消息,比如当发送超时后新建了连接,然后目标节点收到了之前连接发送的消息。所以 Raft 需要处理2个问题:
- 乱序到达的消息;
- 过时的消息。
etcd/raft 在给 Replication 状态的节点发送 msgApp 后,会直接更新 next:
// sendAppend sends RPC, with entries to the given peer.
func (r *raft) sendAppend(to uint64) {
// ...
switch pr.State {
// optimistically increase the next when in ProgressStateReplicate
case ProgressStateReplicate:
last := m.Entries[n-1].Index
pr.optimisticUpdate(last)
pr.ins.add(last)
// ...
}
func (pr *Progress) optimisticUpdate(n uint64) { pr.Next = n + 1 }
在正常情况下,消息顺序到达,follower 就接收 log entries 然后返回给 leader 响应更新 match 和 committed index。乱序到达时,AppendEntries RPC 的 check 就会
失败,follower 返回拒绝消息给 leader,节点会变为 Probe 状态,更新 next = match + 1:
func (pr *Progress) maybeDecrTo(rejected, last uint64) bool {
if pr.State == ProgressStateReplicate {
// the rejection must be stale if the progress has matched and "rejected"
// is smaller than "match".
if rejected <= pr.Match {
return false
}
// directly decrease next to match + 1
pr.Next = pr.Match + 1
return true
}
// ...
}
虽然通过消息的 term 能够过滤掉大部分过时的消息,但节点有可能收到过时和重复的消息,需要处理:
follower: 收到过时或重复的msgApp或snapshot时,返回msgAppResp给leader更新状态。不能忽略,可能是因为之前的msgAppResp发送失败。leader: 只会处理新的消息。
并行操作
有些操作可以并发执行:
leader把entry写入持久存储和给follower发送消息可以并行,这不影响提交entry,只要复制到majority就会提交,即使leader还没有写入。但是follower必须 先写入持久存储,再返回响应。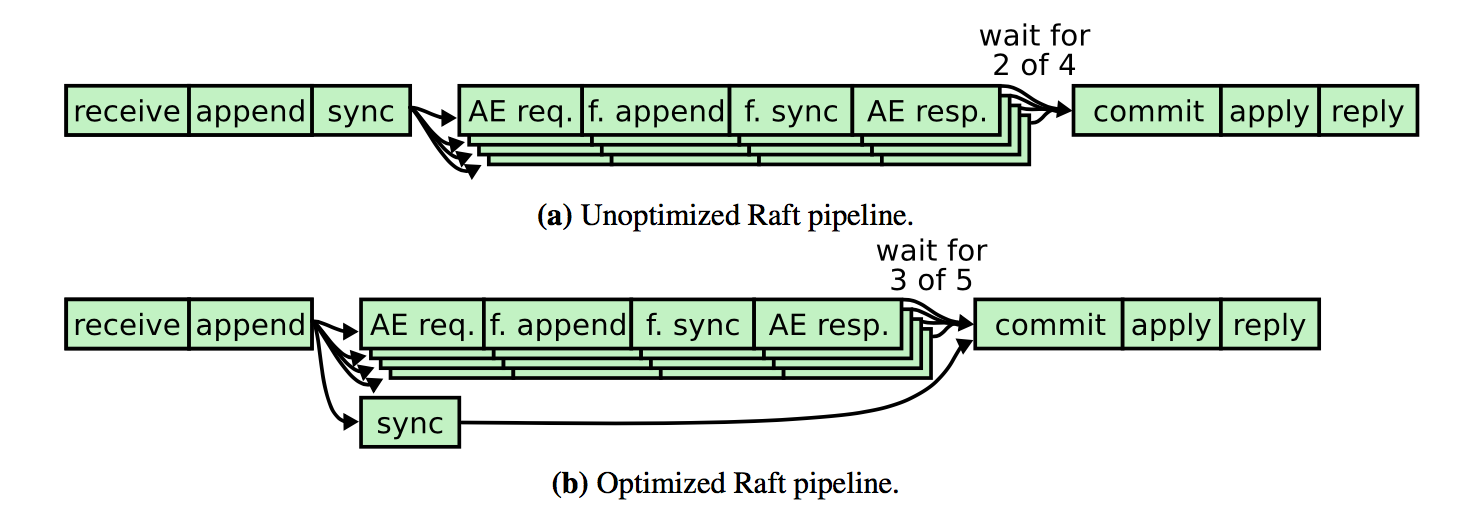
- 当然把
log应用到状态机和发送给客户端响应也可以在另一个线程来执行,与Raft的操作并行。
虽然 client 的一次 request 仍要走完上述所有流程,但对多个 clients 而言,并发和吞吐量上升了。
Persistence
除了 log 和 snapshot,Raft 还有一些状态需要持久化,在节点重启时恢复:
currentTerm:term要保持递增,否则log会有冲突;votedFor: 配合currentTerm防止重启时给多个节点投票。
committed index 和 apply 可以不持久化,启动时设置为 0,接收到其他节点消息时更新 committed index,log 回放时更新 apply。
etcd/raft 返回的 Ready 结构体包含3部分需要持久化: Entries、HardState 和 Snapshot。在把 HardState 写入持久存储之后才可以发送 message,否则有可能在同一 term 给多个节点投票。
type HardState struct {
Term uint64 `protobuf:"varint,1,opt,name=term" json:"term"`
Vote uint64 `protobuf:"varint,2,opt,name=vote" json:"vote"`
Commit uint64 `protobuf:"varint,3,opt,name=commit" json:"commit"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
}
committed index 也会恢复,可以在不接收到其他节点消息时就进行 log 回放,要注意避免重复应用 log,可以通过 Config.Applied 恢复 apply,
不过 Ready 中只会返回存在的 log,若 snapshot 对应的 log 已被删除,也不会重复应用。
etcd/raft 建议按照 Entries、HardState、Snapshot 的顺序持久化,否则有可能重启节点失败。因为 etcd/raft 要求 committed index 在 [snapshot_last_index, log_last_index] 范围内,若
持久化 HardState 后,节点崩溃,有可能造成 committed index 不在范围内,需要修复才能启动:
func (r *raft) loadState(state pb.HardState) {
if state.Commit < r.raftLog.committed || state.Commit > r.raftLog.lastIndex() {
r.logger.Panicf("%x state.commit %d is out of range [%d, %d]", r.id, state.Commit, r.raftLog.committed, r.raftLog.lastIndex())
}
r.raftLog.committed = state.Commit
r.Term = state.Term
r.Vote = state.Vote
}
在重启节点前,用户需要恢复 storage,raft 会根据 storage 恢复状态,包含状态机状态、log、Hardstate、集群信息等:
storage := raft.NewMemoryStorage()
// Recover the in-memory storage from persistent snapshot, state and entries.
storage.ApplySnapshot(snapshot)
storage.SetHardState(state)
storage.Append(entries)
c := &Config{
ID: 0x01,
ElectionTick: 10,
HeartbeatTick: 1,
Storage: storage,
MaxSizePerMsg: 4096,
MaxInflightMsgs: 256,
}
// Restart raft without peer information.
// Peer information is already included in the storage.
n := raft.RestartNode(c)
疑问
- 当
snapshot发送成功或收到follower对snapshot的响应时,此时已经知道了节点的committed index,应该可以直接变为Replicate状态,为什么要变为Probe状态呢,虽然不影响结果。 - 同样的,当
Replication状态发生冲突时,更新的next = match + 1,下一次也不会发生冲突,但还是会进入Probe状态。
留下评论