RocksDB 源码分析 – InlineSkipList
RocksDB 实现了多种可作为 memtable 的数据结构,包括 SkipList、HashSkipList、HashLinkList 和 Vector,可根据场景选择合适的种类,见 MemTable。
这里只看功能最丰富且最常用的 SkipList。
InlineSkipList
memtable 有 3 层封装:
InlineSkipList:最底层的数据结构,提供最基本的读写操作。SkipListRep:MemTableRep的派生类,提供多态。MemTable:提供更多功能。
InlineSkipList 除了支持一写多读,还支持了多写多读,并对插入操作进行了优化。
Node
之所以叫 InlineSkipList,应该是因为 Node 将 key 和链表每层的指针连续存储:
template <class Comparator>
struct InlineSkipList<Comparator>::Node {
private:
// next_[0] is the lowest level link (level 0). Higher levels are
// stored _earlier_, so level 1 is at next_[-1].
std::atomic<Node*> next_[1];
};
格式如下:
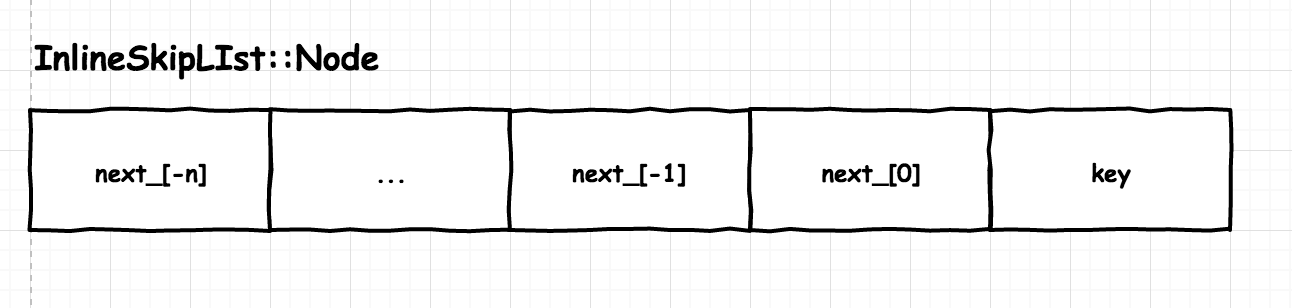
Node 直接存 key,相比于 LevelDB 存 key 的指针,可以减少部分内存使用,更主要的是有更好的 cache locality,访问 next_ 指针时,因为内存连续会把 key 也一并放到 cache 中。而且
在遍历每层 list 时,会 prefetch 后面的 Node:
#define PREFETCH(addr, rw, locality) __builtin_prefetch(addr, rw, locality)
文档 写到作用是:
This function is used to minimize cache-miss latency by moving data into a cache before it is accessed.
效果挺明显,这里记录一下PR#2961:
This change causes following changes result of test:
./db_bench –writes 10000000 –benchmarks=”fillrandom” –compression_type none
from
fillrandom : 3.177 micros/op 314804 ops/sec; 34.8 MB/s
to
fillrandom : 2.777 micros/op 360087 ops/sec; 39.8 MB/s
Insert
都知道 SkipList 插入时,先随机新 Node 的高度,然后要从高层向下从头遍历找到每层的 Prev,最后插入到每层 Prev 的后面。高度 n+1 的 Node 数量是 n 的 1/p,所以插入查找的时间复杂度是 O(log N)。
RocksDB 采用 Splice 结构对插入进行了优化,在部分场景下,插入的时间复杂度是 O(log D),其中 D 是 Splice 到 Key 的距离。
Splice 结构如下:
template <class Comparator>
struct InlineSkipList<Comparator>::Splice {
// The invariant of a Splice is that prev_[i+1].key <= prev_[i].key <
// next_[i].key <= next_[i+1].key for all i. That means that if a
// key is bracketed by prev_[i] and next_[i] then it is bracketed by
// all higher levels. It is _not_ required that prev_[i]->Next(i) ==
// next_[i] (it probably did at some point in the past, but intervening
// or concurrent operations might have inserted nodes in between).
int height_ = 0;
Node** prev_;
Node** next_;
};
其实 Splice 就是保存了上一次插入时遍历的结果,然后在部分场景下可以减少遍历的距离,从而降低时间复杂度。具体细节涉及到几点:
SkipList是从高层到低层遍历,低层遍历的起始位置是由高层决定的,所以如果高层能够缩小查找的范围,那么低层遍历的距离就很小,这也就是RocksDB插入优化的思路。Splice的循环不变式如上面注释,意思是低层的范围比高层的范围小,这是由SkipList结构决定的。Splice在插入完成后,会设置所有prev是新插入的Node,保证了Splice在插入完成后每层的紧凑。
在插入时,会从低层到高层遍历 Splice,若发现某一层紧凑包围了 key,那么比这层高的都紧凑包围了这个 key,比这层低的从这点开始遍历即可,所以复杂度为 O(log D)。
但如果 splice 不包围 key 的话,因为多了遍历 Splice 的操作,常数因子就会增大,所以这个优化由参数 allow_partial_splice_fix 决定,为 true 时会强制遍历 Splice 每层,
而为 false 时如果最低层不包围的话就会退出遍历,然后从最高层从头开始向下重新计算 Splice,也就是 O(log N) 的复杂度。Insert 默认为 false,但如果是顺序插入,仍然是 O(1) 的复杂度,
InsertWithHint 会以用户传入的 Splice 为参数,且 allow_partial_splice_fix 为 true。
InsertConcurrently
RocksDB 是支持并发写的,目前只有 InlineSkipList 实现了,一写多读实现的逻辑和 LevelDB 相同,不赘述了,并发写的实现也很简单,每一层使用 CAS 来插入 Node,失败时重新计算这一层的 Splice 并重试,
CAS 保证了其他线程的修改可见。
留下评论