Redis源码阅读(三) – sds
sds在Redis内使用广泛,除了用来保存字符串值之外,还被用作缓冲区。sds的实现很简单,如下:
typedef char *sds;
/* Note: sdshdr5 is never used, we just access the flags byte directly.
* However is here to document the layout of type 5 SDS strings. */
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr5 {
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, and 5 msb of string length */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr8 {
uint8_t len; /* used */
uint8_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr16 {
uint16_t len; /* used */
uint16_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr32 {
uint32_t len; /* used */
uint32_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr64 {
uint64_t len; /* used */
uint64_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
结构
__attribute__ ((__packed__))是gcc提供的扩展,文档如下:
The packed attribute specifies that a variable or structure field should have the smallest possible alignment–one byte for a variable, and one bit for a field, unless you specify a larger value with the aligned attribute.
也就是结构体内部紧凑排列,不会有padding,可以节省空间。char buf[]使用了C99的特性:柔性数组,不会占据结构体空间,当分配多余的内存时,会相当于数组使用。由此不难猜出,sds是一种紧凑、连续的结构,
sds头和buf一同分配、释放。传统的做法是sdshdr和data分为两部分,Redis这样做有两个好处:
- 方便的转换不同类型的
sds cache line优化:在 cpu 访问数据的时候,会读入连续内存,当数据量小的时候,sdshdr和data一起读入,可以降低cache miss。
创建
创建sds的代码如下:
/* Create a new sds string with the content specified by the 'init' pointer
* and 'initlen'.
* If NULL is used for 'init' the string is initialized with zero bytes.
*
* The string is always null-termined (all the sds strings are, always) so
* even if you create an sds string with:
*
* mystring = sdsnewlen("abc",3);
*
* You can print the string with printf() as there is an implicit \0 at the
* end of the string. However the string is binary safe and can contain
* \0 characters in the middle, as the length is stored in the sds header. */
sds sdsnewlen(const void *init, size_t initlen) {
void *sh;
sds s;
char type = sdsReqType(initlen);
/* Empty strings are usually created in order to append. Use type 8
* since type 5 is not good at this. */
if (type == SDS_TYPE_5 && initlen == 0) type = SDS_TYPE_8;
int hdrlen = sdsHdrSize(type);
unsigned char *fp; /* flags pointer. */
sh = s_malloc(hdrlen+initlen+1);
if (!init)
memset(sh, 0, hdrlen+initlen+1);
if (sh == NULL) return NULL;
s = (char*)sh+hdrlen;
fp = ((unsigned char*)s)-1;
switch(type) {
case SDS_TYPE_5: {
*fp = type | (initlen << SDS_TYPE_BITS);
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_8: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(8,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = initlen;
*fp = type;
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_16: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(16,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = initlen;
*fp = type;
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_32: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(32,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = initlen;
*fp = type;
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_64: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(64,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = initlen;
*fp = type;
break;
}
}
if (initlen && init)
memcpy(s, init, initlen);
s[initlen] = '\0';
return s;
}
从代码中可以看出,有下面几个特点:
sh = s_malloc(hdrlen+initlen+1): 首先获取sds类型,然后分配连续的内存空间,包含最后的\0s[initlen] = '\0':sds存放以\0结尾的字符串s = (char*)sh+hdrlen: 最后返回的是s,指向的是以\0结尾的字符数组,所以sds兼容了C标准库里的字符串操作
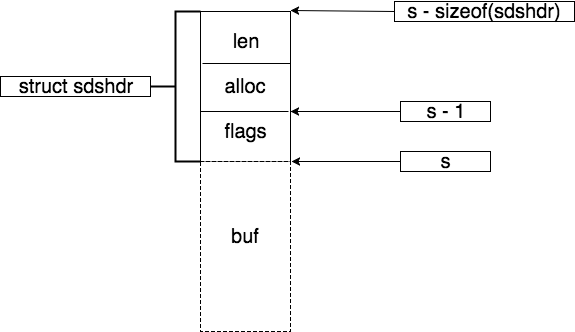
释放
释放代码如下:
/* Free an sds string. No operation is performed if 's' is NULL. */
void sdsfree(sds s) {
if (s == NULL) return;
s_free((char*)s-sdsHdrSize(s[-1]));
}
使用柔性数组的特点,可以很方便获取到分配空间的起点,一次释放,避免了传统实现的二次分配、释放。sds代码比较简单,不再赘述。
留下评论